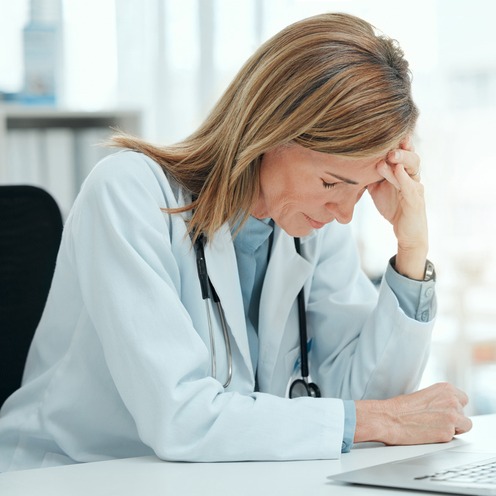
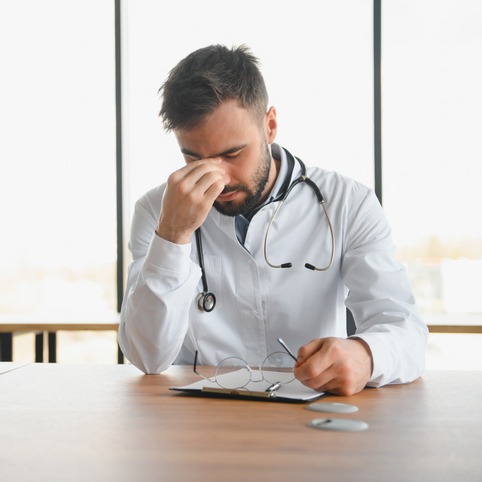
I am a victim of physician burnout.
The pressures of maintaining a solo private practice wore me down to the point of mental and physical breakdown. I stayed in the profession much longer than I should have. I needed to step away for the sake of my health and the stability of my family.
Physician burnout is a critical issue in healthcare, with recent statistics underscoring its prevalence and impact. According to a 2021 report by the American Medical Association, over 40% of physicians experience burnout symptoms, with frontline specialties such as emergency medicine, critical care, and internal medicine reporting the highest rates. The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated the issue, leading to increased workloads, emotional stress, and concerns for personal safety, all of which contribute to heightened levels of burnout among healthcare professionals. Burnout not only affects the well-being of physicians but also has significant implications in patient care. Studies have linked it to decreased job satisfaction, an increase in medical errors, and higher turnover rates. Addressing physician burnout requires systemic changes within healthcare organizations. These changes should include improvements in work-life balance, enhanced support for mental health, and the implementation of technological solutions to streamline workflows and reduce administrative burdens.
Artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine was relatively new when I retired. I have often wondered how long my career would have lasted if I had started practicing today rather than 30 years ago.
AI has the potential to alleviate some aspects of physician burnout by automating routine tasks, streamlining administrative processes, and assisting in clinical decision-making. Here are some ways AI could help mitigate physician burnout:
Administrative Task Automation
I spend a significant portion of my working day on paperwork, documentation, and other administrative tasks unrelated to the practice of medicine. I was never trained in administration, nor did I anticipate the necessity of engaging in such tasks. AI-powered tools, leveraging natural language processing (NLP), have emerged as a transformative force in healthcare documentation, potentially revolutionizing the way patient encounters are recorded and processed. NLP algorithms are capable of efficiently converting spoken or written language into structured data, thereby automating the tedious documentation tasks that consume much of my time. By transcribing and summarizing patient encounters in real-time or near-real-time, these AI systems significantly reduce the burden of manual note-taking and documentation, allowing physicians like myself to devote more attention to direct patient care.
Furthermore, NLP-powered tools can extract critical information from clinical narratives, including symptoms, diagnoses, treatments, and outcomes, and organizing it into structured formats that are compatible with electronic health records. These tools not only save time but also enhance the accuracy and completeness of patient records. This facilitates improved communication among healthcare providers and boosts the continuity of care. Consequently, physicians are able to devote more attention to critical aspects of patient management and decision-making, ultimately enhancing the efficiency and quality of care. Additionally, these AI-driven documentation solutions can potentially reduce transcription errors and inconsistencies, leading to improved data integrity and better utilization of healthcare resources.

Clinical Decision Support
AI systems, equipped with advanced machine learning algorithms, can sift through vast amounts of medical data, including patient records, diagnostic images, genomic information, and findings from clinical research. By analyzing this extensive pool of information, AI can generate personalized treatment recommendations tailored to the unique characteristics, medical histories, and preferences of individual patients. These recommendations may encompass suggested medications, dosage adjustments, treatment protocols, or lifestyle interventions, all optimized for the specific needs and circumstances of each patient. Furthermore, AI can continuously monitor patient data in real-time, identifying potential issues or conflicts in care such as drug interactions, contraindications, or deviations from established protocols. By providing timely alerts and decision support, AI enables physicians to make more informed clinical decisions, thereby reducing the likelihood of errors and adverse events. This proactive approach not only enhances patient safety but also improves outcomes by ensuring that interventions are aligned with evidence-based best practices and personalized to each patient's condition. Consequently, physicians can approach their treatment decisions with greater confidence, leading to reduced stress and burnout levels as they navigate complex clinical scenarios with the support of AI-driven insights. Ultimately, the integration of AI into clinical workflows is set to transform healthcare delivery by optimizing decision-making processes, enhancing patient outcomes, and alleviating the burden on healthcare providers.
Predictive Analytics
AI algorithms are adept at mining vast repositories of patient data to uncover subtle patterns and correlations that may not be immediately apparent to human observers. By analyzing diverse data sources, including electronic health records, imaging studies, genetic profiles, wearable device data, and environmental factors, AI can detect early indicators of potential health risks or disease progression. These algorithms can identify predictive biomarkers, risk factors, and clinical trajectories associated with specific conditions, enabling physicians to anticipate complications and intervene preemptively. For instance, AI can flag patients at high risk of developing complications such as sepsis, heart failure exacerbations, or diabetic ketoacidosis, based on subtle changes in vital signs, laboratory values, or clinical parameters.
With these early warnings and risk assessments, AI empowers physicians to initiate timely interventions, adjust treatment plans, or implement preventive measures to mitigate risks and prevent adverse outcomes. This proactive approach not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces the burden on physicians by minimizing the need for reactive, crisis-oriented care. Rather than constantly responding to emergencies, physicians can take a more strategic and proactive stance, focusing on preventive strategies and targeted interventions tailored to each patient's unique risk profile. Consequently, healthcare organizations can achieve more efficient resource allocation, lower healthcare costs, and improved patient satisfaction, while physicians experience less stress and burnout from managing preventable crises. Overall, AI-driven predictive analytics enable healthcare providers to transition from a reactive model of care to a proactive paradigm centered on early detection, prevention, and personalized intervention, thereby enhancing the quality, efficiency, and sustainability of healthcare delivery.
Workflow Optimization
AI's potential to optimize clinical workflows extends beyond documentation and decision-making support; it encompasses the entire patient care journey, from initial appointment scheduling to post-treatment follow-ups. AI-powered systems can revolutionize administrative tasks by automating appointment scheduling processes, seamlessly coordinating care plans across multiple healthcare providers and facilities, and intelligently prioritizing tasks based on urgency and complexity. These systems leverage algorithms that consider various factors, such as patient preferences, availability of healthcare providers, clinical guidelines, and resource constraints, to optimize scheduling and resource allocation. By efficiently managing appointments and care coordination, AI eliminates inefficiencies, reduces wait times, and minimizes scheduling conflicts, ensuring patients receive timely and appropriate care while maximizing healthcare providers' productivity.
Moreover, AI can assist physicians in triaging tasks and patient cases, identifying urgent or high-priority issues that require immediate attention, and delegating routine or less critical functions to other care team members. This strategic allocation of resources improves patient flow and throughput and enables physicians to focus their time and expertise on cases requiring specialized attention. As a result, physicians experience less cognitive overload, can better manage their workload, leading to increased job satisfaction, reduced burnout, and ultimately, enhanced quality of care for patients. By streamlining clinical workflows and optimizing resource utilization, AI empowers healthcare organizations to deliver more efficient, patient-centered care while alleviating the administrative burden on physicians and fostering a more sustainable healthcare ecosystem.
Virtual Assistants and Chatbots
AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots have the capacity to handle routine inquiries, schedule appointments, and provide patients with basic medical information, thereby reducing interruptions and administrative tasks for physicians.
However, while AI shows promise in mitigating some factors contributing to physician burnout, it is not a cure-all solution. I cannot honestly say whether AI would have saved my career, but it certainly could have been beneficial.
Challenges in implementation, such as data privacy concerns, interoperability issues, and resistance to change, must be addressed. Additionally, it's crucial to view AI as a tool meant to augment human capabilities rather than replace human interaction and decision-making in healthcare. Comprehensive strategies that tackle systemic issues, including workload management, work-life balance, and organizational culture, are essential for effectively addressing physician burnout.
Rely on PlanetDrugsDirect.com to Buy Your Medication Online
As a trusted prescription referral service, we offer important benefits whenever you order online. Each of our partner pharmacies and/or government-approved dispensaries is committed to providing the best experience possible of any online prescription referral service on the internet. We offer:
Low prices
Quick turn-around times
Generic and brand-name medications
Unparalleled customer service
Sources
Awan, O. (2023, April 12). Artificial Intelligence and Its Potential to Combat Physician Burnout. Forbes. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/omerawan/2023/04/12/artificial-intelligence-and-its-potential-to-combat-physician-burnout/
Lovelace Jr., B. (2023, August 7). Hospitals use AI like Microsoft Nuance’s DAX app to fight burnout. CNBC. Retrieved from https://www.cnbc.com/2023/08/07/hospitals-use-ai-like-microsoft-nuances-dax-app-to-fight-burnout.html
Landi, H. (n.d.). How AI is decreasing burnout, allowing health professionals to work at the top of their license. FierceHealthcare. Retrieved from https://www.fiercehealthcare.com/ai-and-machine-learning/how-ai-decreasing-burnout-allowing-health-professionals-work-top-their
American Association of Medical Colleges. (n.d.). Can artificial intelligence improve doctor-patient visits and reduce burnout? AAMC. Retrieved from https://www.aamc.org/news/can-artificial-intelligence-improve-doctor-patient-visits-and-reduce-burnout
 Medically reviewed by
Medically reviewed by